|
Testing Your pH Levels
Body pH
and Blood pH as Indicators of Health
Below
is what you will hopefully find useful in finding out more about
your body's pH and how to test it. There are different opinions
about optimum pH and this is one of them. Nevertheless, there is a
strong and growing acceptance that we are, in general, over acidic
and that excess acidity is the root cause of many of the so-called
aging diseases.
The
Importance of pH Balance in Maintaining Health
" Thus
the saliva pH parallels the extra cellular fluid ... pH paper test
using saliva represents the most consistent and most definitive
pHysical sign of the ionic calcium deficiency syndrome ... The
saliva pH of the non-deficient and healthy person is in the 7.5 to
7.1 slightly alkaline range. The range from 6.5 which is weakly
acidic to 4.5 which is strongly acidic represents states from mildly
deficient to strongly deficient, respectively.
Most
children are dark blue, a pH of 7.5. Over half of adults are
green-yellow, a pH of 6.5 or lower, reflecting the calcium
deficiency of aging and lifestyle defects. Cancer patients are
usually a bright yellow, a pH of 4.5, especially when terminal."
The Calcium Factor: The Scientific Secret of Health and Youth,
Carl J. Reich, M.D., Gilliland Printing Inc., Arkansas City, Kansas,
1996.
pH
Balance - What is the Healthy pH Range?
The pH
scale ranges from 0 (the highest acidic) to 14 (the most alkaline).
A solution with a pH of 7 is neutral. The pH scale goes from 0 to 14
and is logarithmic, which means that each step is ten times the
previous. In other words, a pH of 5 is 10 times more acid than 6,
100 times more acid than 7 and 1,000 times more acid than 8. In this
light, you can see how a slight change in your pH value can have a
great impact on your internal environment and, ultimately, your
health. When healthy, the blood pH is 7.365, the pH of spinal fluid
is 7.4, and the saliva pH is 7.4. This ideal blood pH measurement
means it is more alkaline than acid.
In the
absence of oxygen, glucose undergoes fermentation to lactic acid.
Our bodies simply can not fight disease if our body pH balance is
compromised.
It has been determined that an alkaline body is more conducive to
health and well-being than an acidic one. An undesirable pH can lead
to a variety of negative health effects. A body that tends toward
acidity heightens the risk for infections from bacteria, yeast,
parasites, and viruses. All of these seek out and thrive in an acid
environment.
Not
only are you more susceptible to infections such as colds and the
flu but also degenerative diseases like cancer, arthritis, heart
disease and osteoporosis are promoted if your pH is consistently
acid.
Furthermore, populations of bacteria, fungi, etc. may be thriving
throughout your body without causing acute disease, yet producing
copious acid waste products. These stealth infections may underlie a
variety of degenerative conditions. Bacteria are found in arthritic
joints, arterial plaque, and many other places. If disease is to be
prevented or successfully managed, an acid pH must be overcome.
To maintain good health the body is
constantly seeking to get rid of the excess acids that irritate the
tissues and deplete them of minerals. One of the principal systems
it uses for this purpose is the renal system (kidneys).
There is a strong correlation
between the pH of the body's internal environment and that of the
urine and saliva: urine and saliva become acidic when the body's
internal environment becomes acidic. You can discover the pH of
these fluids by using pH test strips.
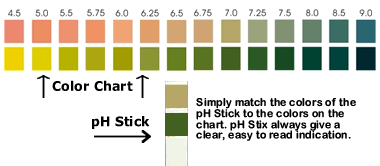
SALIVA: Take a saliva reading in the morning.
If the pH level is lower than 6.75, then your alkaline mineral
reserves are low.
URINE: Test your first urination in the morning. If
the pH level is lower than 6.25, then your alkaline mineral reserves
are low. You will likely see urine pH
become more alkaline as the day progresses.
|